ABS Resin
What is ABS Resin?
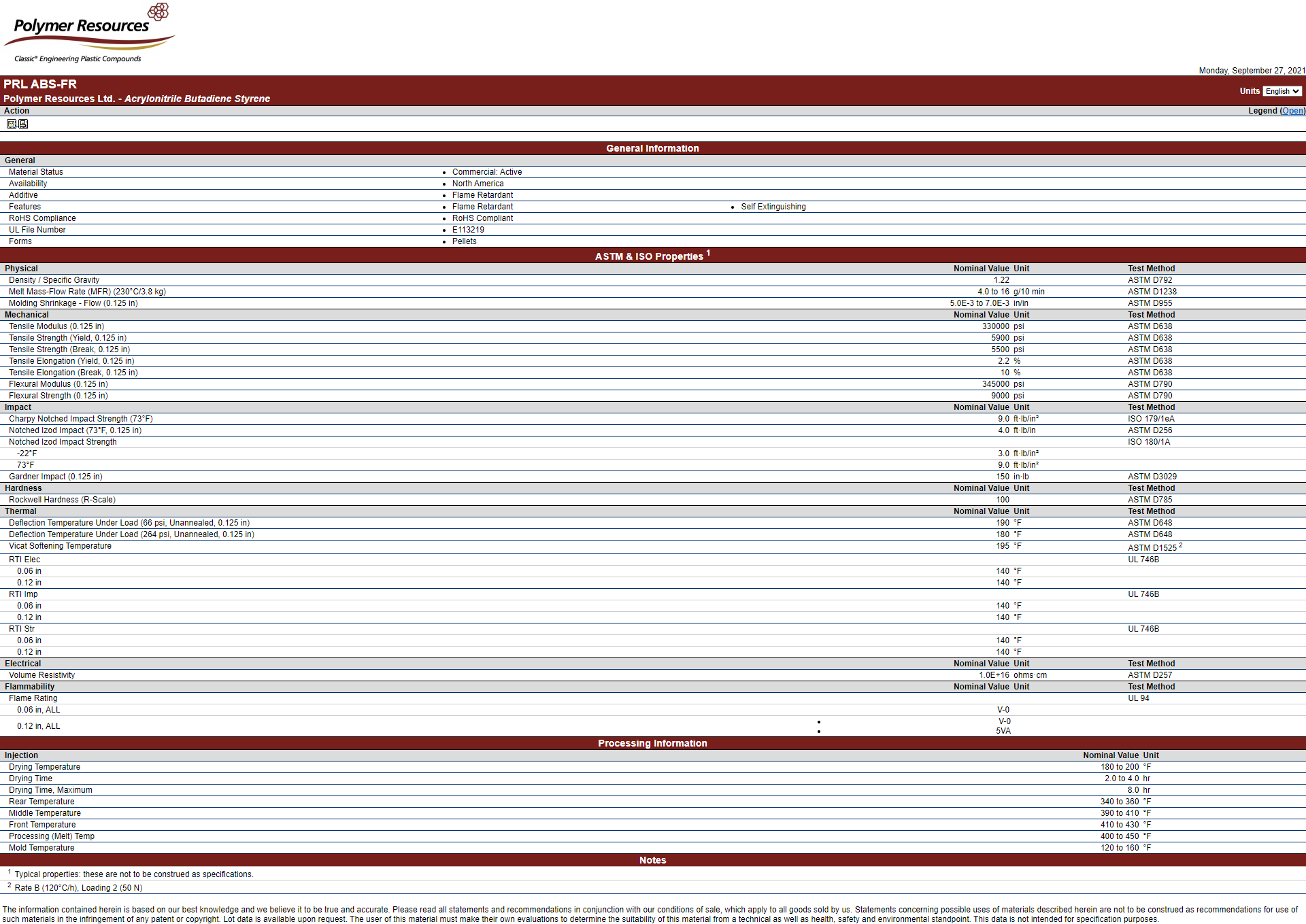
ABS (acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene terpolymer) is an amorphous engineering thermoplastic material that provides a good balance of toughness and rigidity. Each component of the terpolymer contributes specific features to the overall performance of this material. The styrene component provides gloss and rigidity while the butadiene component provides excellent impact properties. The acrylonitrile component contributes to melt strength and chemical resistance. ABS is resistant to attach to both mineral acids and bases. ABS is also resistant to both vegetable and mineral oils. ABS holds up well to most household cleaners.
Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene is available in both injection molding and extrusion grades. Additionally, ABS is easy to process. Compounding technology allows a wide variety of colorants to be compounded into ABS. This allows production in a wide range of custom colors. Applications for ABS products can be extended by the addition of additives such as stabilizers, flame retardants, and reinforcing fillers.
ABS Variations
Most common variations of ABS material includes General Purpose ABS, High Impact ABS, Low Viscosity ABS, Plate-able ABS, ABS FR and many more. The modification of its properties is possible with the use of additives, modifiers and reinforcing agents.
ABS Resin Features
- Excellent ductility
- High Impact strength
- Extremely tough and rigid
- Dimensional stability
- High tensile strength
- Heat and chemical resistance
- Electroplatable
- High and low temperature performance
-
Additives, Modifiers, and Reinforcing Agents:
- Additives – UV stability, easy release (mold releases), colorants, and other stability additives
- Modifiers – Flame retardants, impact modifiers, flow enhancers
- Reinforcing Agents – Glass fibers, mineral fillers
PRL Alternative Material Solutions to
Example: If you’re looking for Ineos Styrolution alternatives or Sabic alternatives: find the product in the relevant row and look to the leftmost row to find our alternative.
PRL Grades
- PRL ABS-GP1
- PRL ABS GP IM
- PRL ABS GP HH
- PRL ABS FR
- PRL ABS G10
- PRL ABS G20
- PRL ABS G30
- PRL ABS FR UV (f2)
INEOS Styrolution
- Lustran® 248, 448, 648
- Absolac® 100
- Elix® ABS H801
- Absolac® 30 GF20
- Absolac® 30 GF30
- Lustran® 448
SABIC
- MG38, MG47, MG94
- Cycolac® MG 38
- Cycolac® X15, X17, X37
- FR15, FR23, FR30
- Thermocomp® AF002
- Thermocomp® AF004
- Thermocomp® AF006
- Cycolac® FR15U
Trinseo
- Magnum® 3504; 3513
- Magnum® 375HH
- Celex® 720
- Celex® 730
PRODUCT Q&As
Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of ABS resin?
This material can be injection molded, blow molded or extruded, and features a broad processing window. It can also be used in electroplating processes.
The main disadvantage of ABS is poor resistance to weathering. Long-term exposure to light causes it to yellow. Although ABS is not inherently flame retardant, flame retardant grades can be produced by incorporating additives.
Q. How strong is ABS resin?
Q. What is ABS resin used for?
Q. Can ABS materials be used for 3D printing?
Our Mission
My mission at Polymer Resources has not changed since I founded this company more than four decades ago. It includes continuing our tradition of financial stability, sustainable growth and visionary leadership that compounds success for customers, suppliers and employees. It also means proudly manufacturing our products in America, and making them available to the global marketplace.
Les Klein, Chief Executive Officer, Polymer Resources, Ltd.
 Print
Print Download
Download Email
Email